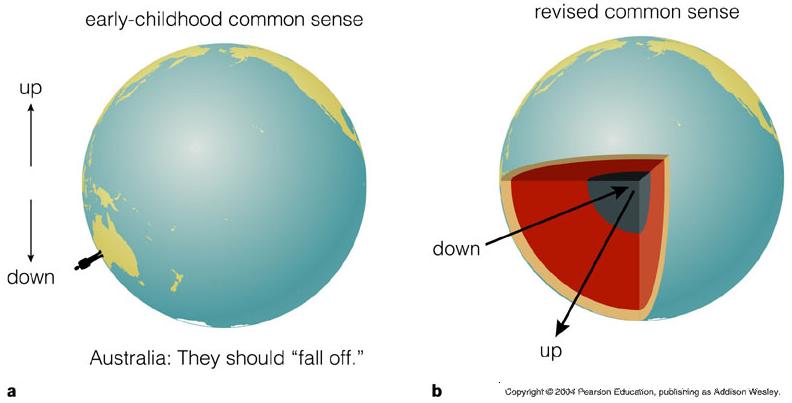
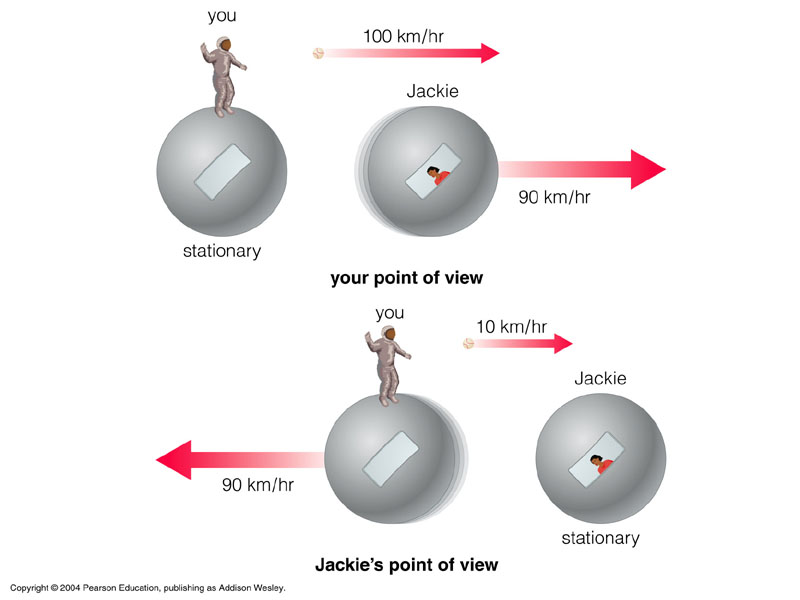
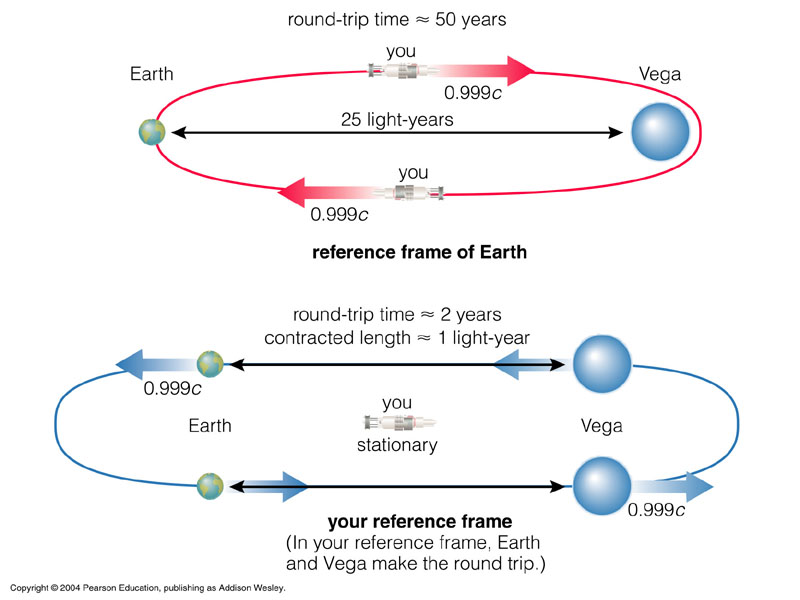
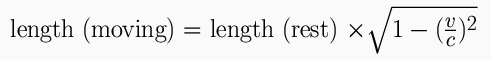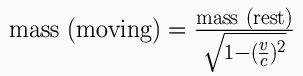- time differs in different reference frame
- time runs slower in the reference frame of anyone moving relative to you

- sequence of events are not absolute and dependent on the observer's frame
A sample problem is here
|
|
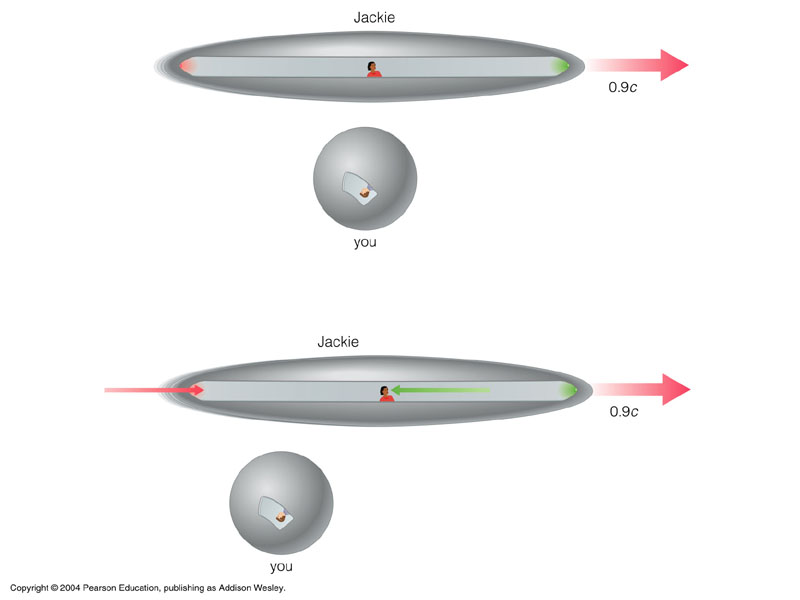
- lengths (or distances) differs in different reference frame
- lengths of objects in the reference frame of anyone moving relative to you are shorter in their direction of motion
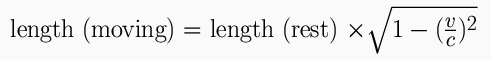
|
|
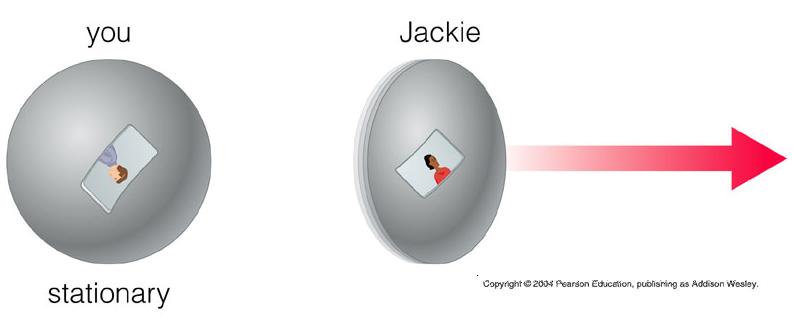
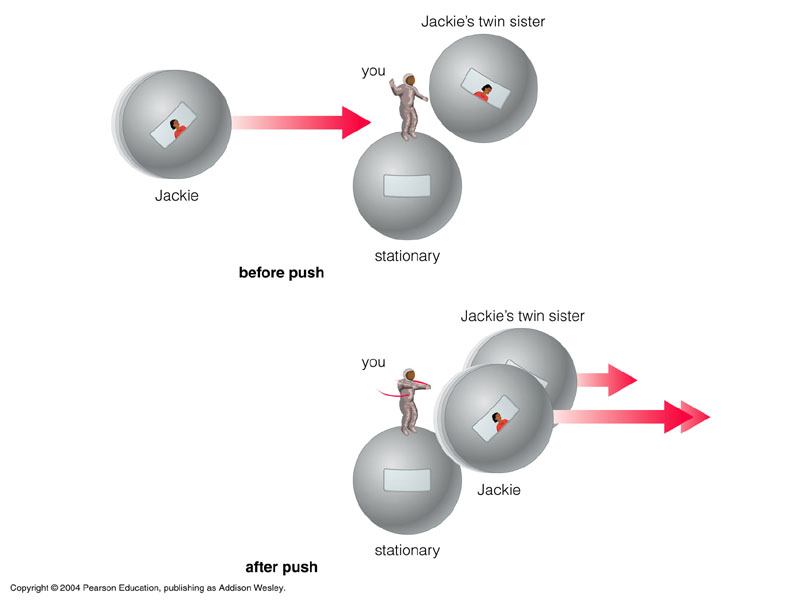
- objects moving relative to you have greater mass than they have at rest.
- the kinetic energy (mass) of an object with velocity approaching the speed of light would approach infinity.
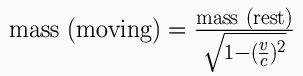
|
|