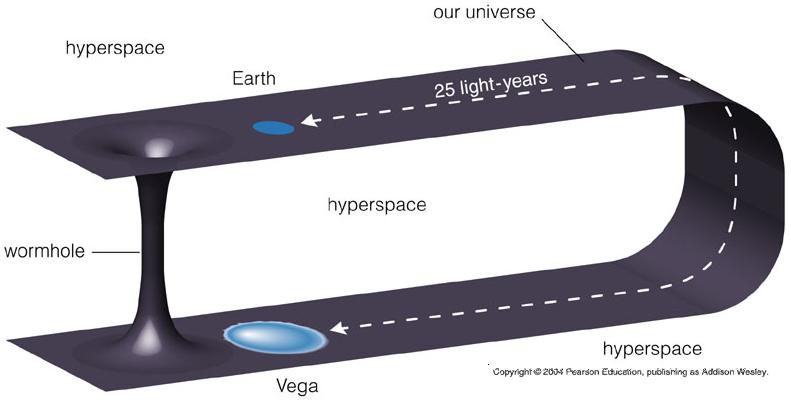
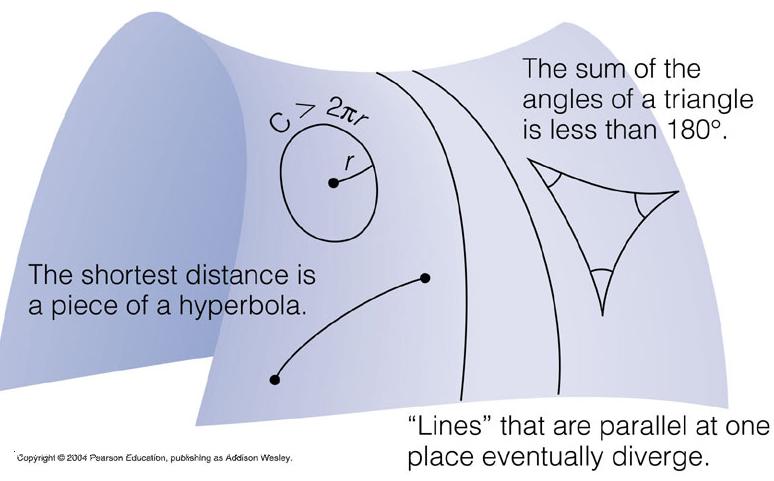
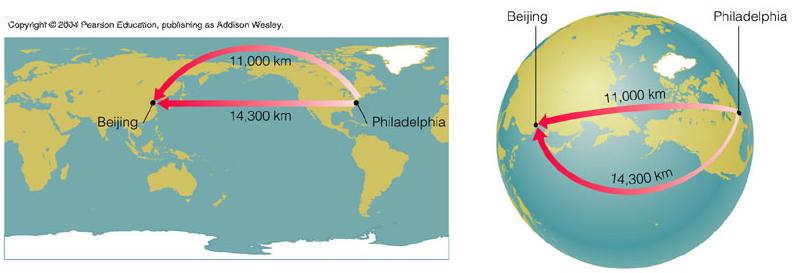
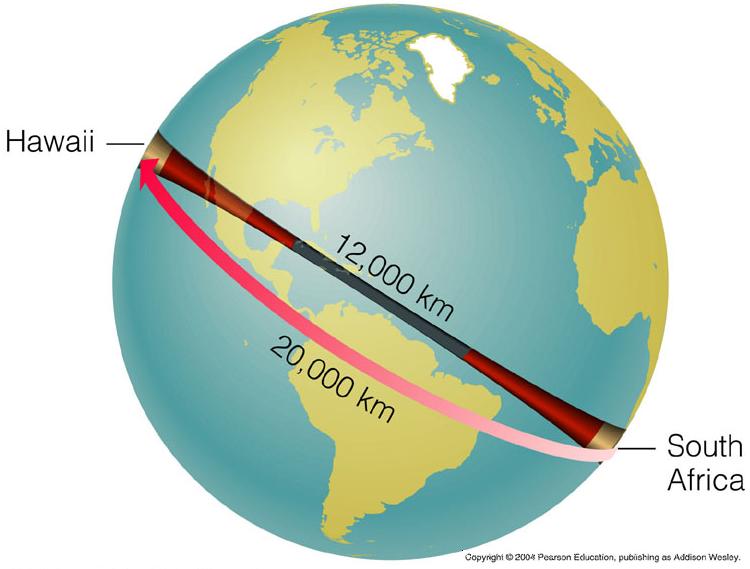
The shortest path in a curved space may not necessarily be a "straight line".

|
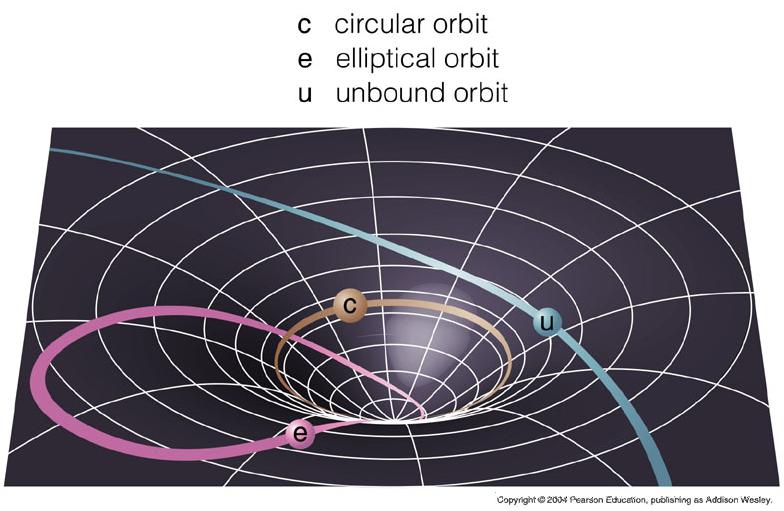
Mercury's Orbit
- Mercury's orbit slowly precesses around the Sun.
- cannot be explained by Newton's law of gravity.
- Time runs slower and space is more curved on the part of Mercury's orbit that is nearer the Sun.
|
|
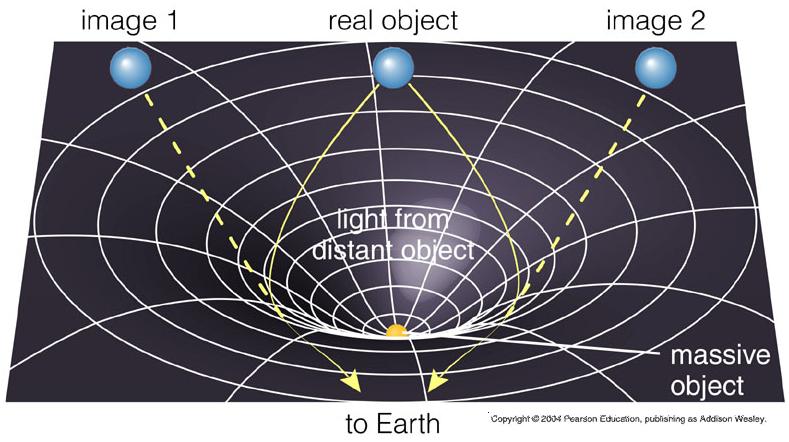
- The curvature of space near a massive object (e.g. Sun) forces
the light beam passing near it to bend, much like a lens.
- Changes in angular separation between stars were measured to change near the Sun during the solar eclipse in 1919 by Sir Arthur Eddington.
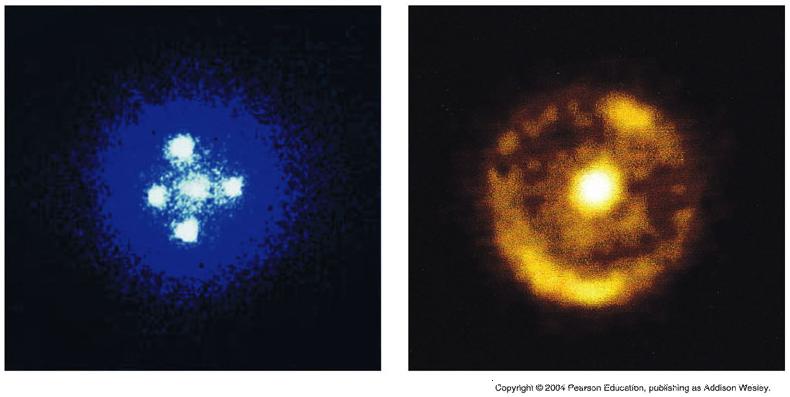
- Trajectories of light from distant stars or galaxies
are bent by the gravitational field of a massive object located along the
line-of-sight, producing multiple images or a ring of images.
|
|
Gravitational Waves
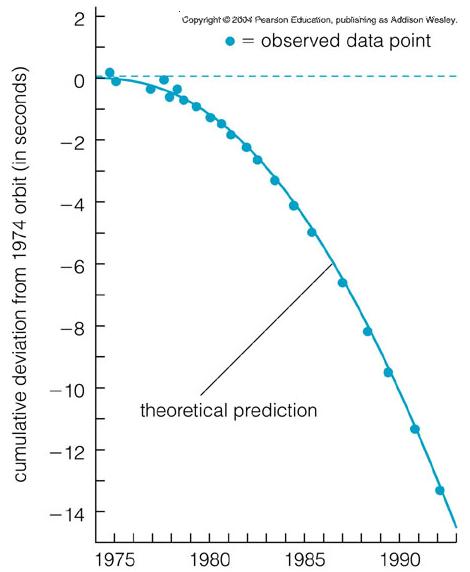
- The orbital periods of binary pulsars gradually decreases with time.
- Two massive stars orbiting each other closely and rapidly generate ripples of curvature in space (or gravitational waves).
- In 1974, Russell Hulse and Joseph Taylor (of UMass) measured the decreases in the orbital periods of binary pulsars and explained it to be a consequence of orbital energy loss through gravitational waves.
|



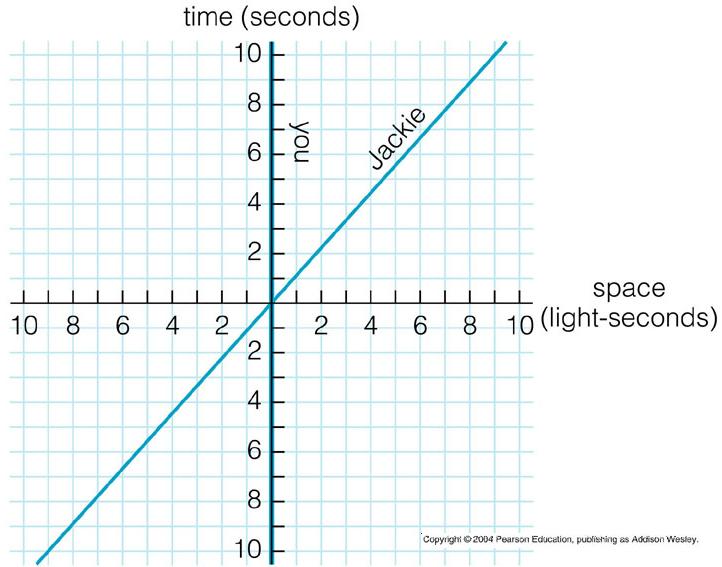 _
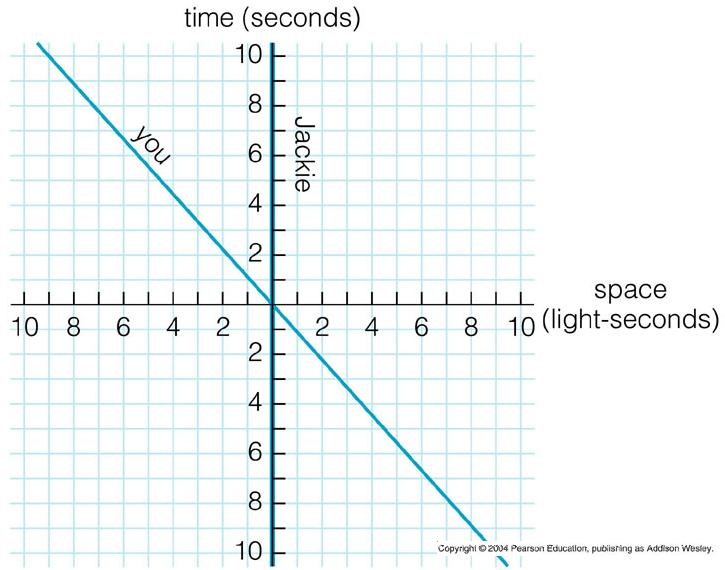
_
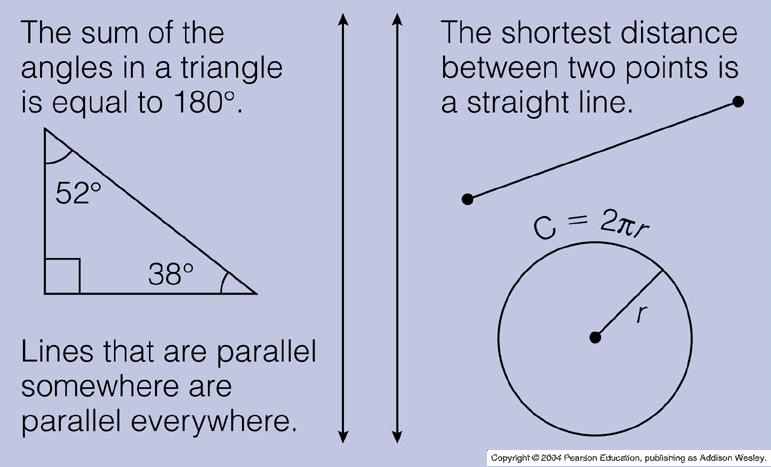
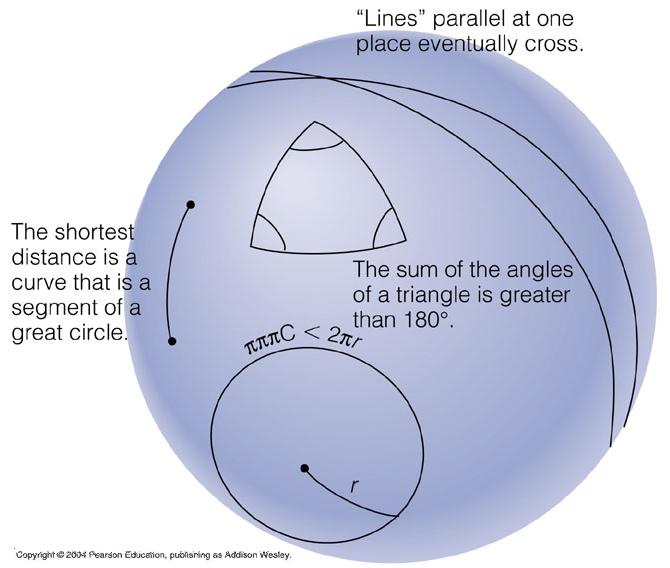

 __
__




 __
__