Lecture 4
Fall 2006
View from A Spinning Planet
Key Concepts:
- What causes the phases of the Moon?
- Why do solar and lunar eclipses occur?
- What is a retrograde motion and why is it important?
Phases of the Moon
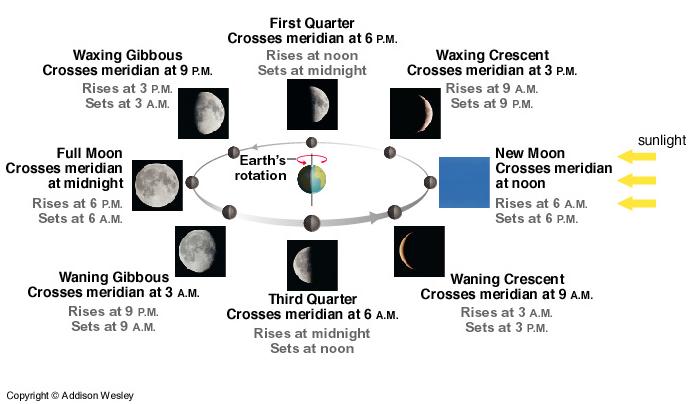
Earth from the Moon>
Earth and Moon from Mars>
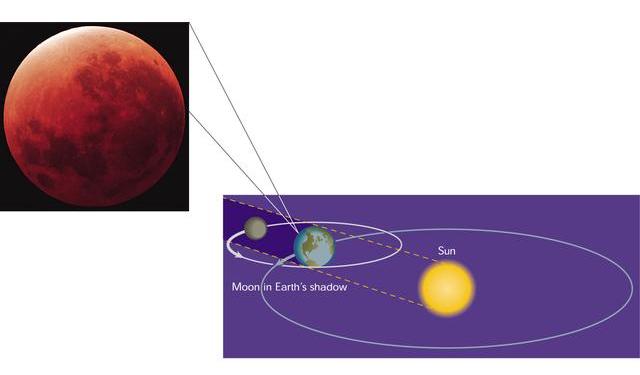
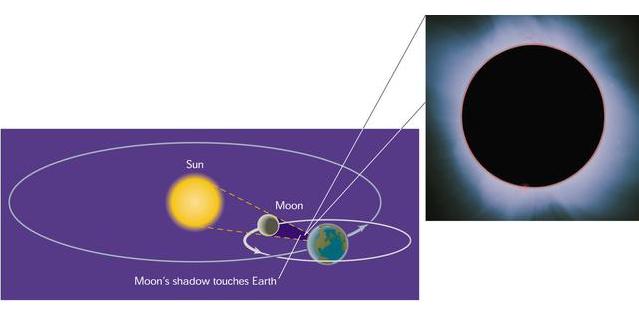
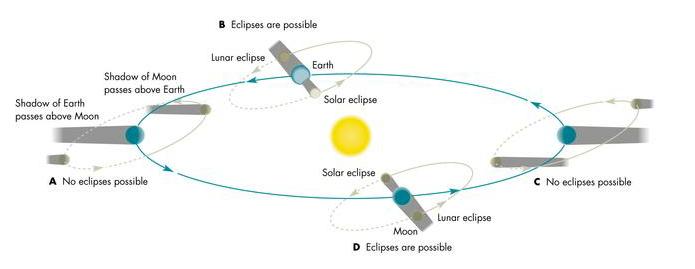
Eclipse
- Lunar Eclipse: Sun --> Earth --> Moon ("Shadow of the Earth")
- Solar Eclipse: Sun --> Moon --> Earth ("Shadow of the Moon")

- Quiz 4b: Once in a blue moon?
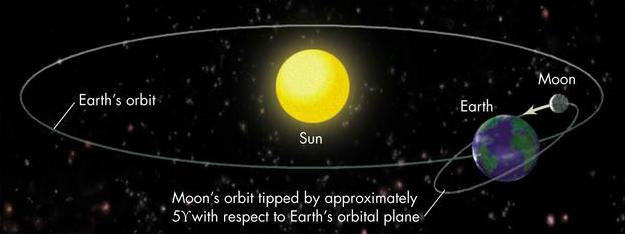
- Why eclipses do not happen every month?
- Moon's orbit tipped by about 5 degrees with respect to Earth's orbital plane
- Eclipse "season": Moon orbit crosses Earth orbital plane only twice a year
- Moon's diameter only about 1/4 of the Earth diameter
- Moon's distance only about 1/100 of the distance to the Sun

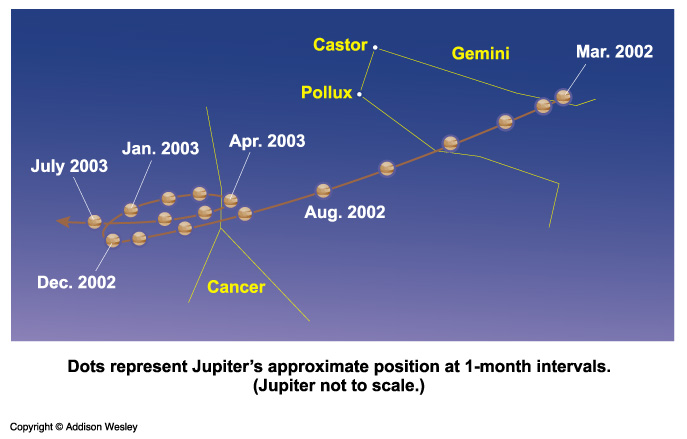
- Like the Sun and the Moon, the planets generally appear to move slowly
eastward through the zodiac (OK for
a geocentric model as well).
- Occasionally, some planets appear to move
westward relative to the stars!
(a challenge for a geocentric model)
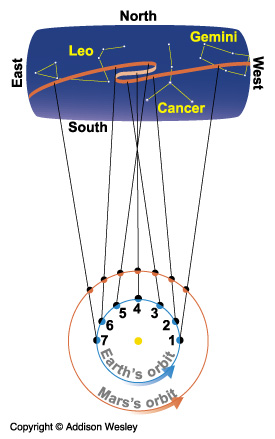
- As shown by the diagram on the right side, this can be explained
by the projected locations of planets in a heliocentric
solar system model.
- See this Java applet demonstration at UIUC as well.
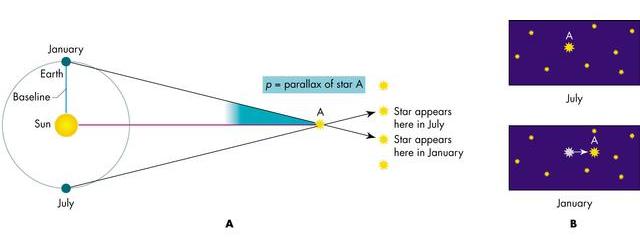
Stellar Parallax
- Apparent Shift in the position of a nearby star
as we look at it from different places in the Earth's orbit.
- Parallax should not exist in a geocentric model.
- The more distant the star, the smaller the parallax --
a method to derive distances to stars!

Reading assignment for next lecture: Chapter 3 (p.64-p.82)










